Breweries in Galveston Texas: Regional Craft Beer Adventures
Distillery Characteristics Unveiled: a Trip With the Science and Art of Spirits Production
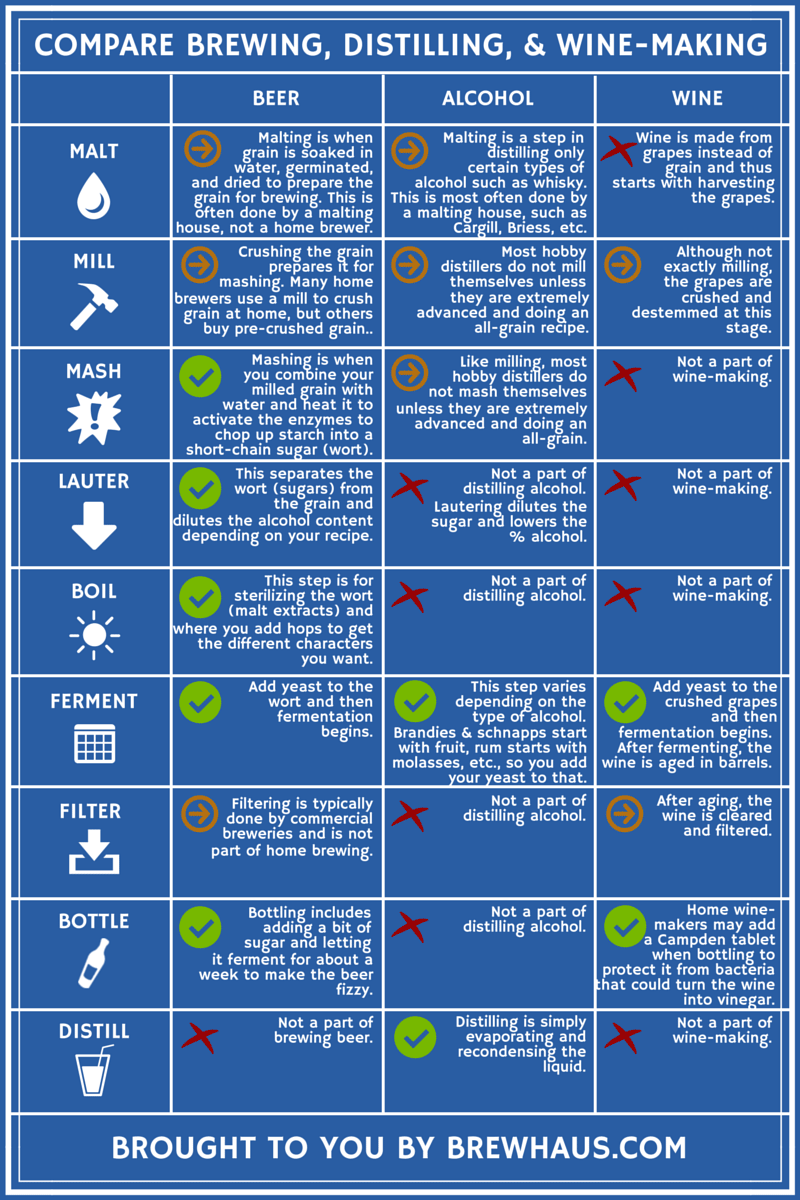
As the drapes are drawn back on the complex globe of distillery dynamics, a remarkable world emerges where science and art assemble to produce the spirits we relish. The marital relationship of practice and technology in spirits manufacturing reveals a tapestry woven with threads of workmanship and technological developments.
The Chemistry of Distillation
The chemistry of distillation, a basic procedure in the manufacturing of spirits, includes the splitting up of components based on their various boiling factors. This distilled fluid, understood as the "heart cut," contains the wanted alcohol content and flavor compounds.
During purification, three main fractions are obtained: the "heads," which have unstable compounds and greater alcohols that can be dangerous if consumed in big amounts; the "hearts," the treasured portion with the desired ethanol and flavor account; and the "tails," which contain larger substances and fusel alcohols. Proficient distillers need to very carefully keep an eye on the temperature level and circulation prices to divide these portions effectively, guaranteeing a high-grade end product. The chemistry of purification is a fragile interaction of heat, vaporization, and condensation that transforms a straightforward liquid combination right into a facility and refined spirit.
Artisanal Craftsmanship in Spirits Making
Among the globe of spirits production, artisanal workmanship plays an essential duty in elevating the top quality and personality of distilled beverages (Galveston Liquor). Artisanal craft distillers concentrate on small-scale, hands-on production approaches, commonly utilizing typical methods that have actually been passed down via generations. These committed craftsmen and women focus on top quality over quantity, paying careful interest to every step of the distillation process
Artisanal craftsmanship in spirits making involves a deep understanding of the raw materials utilized, such as fruits, botanicals, or grains, and exactly how their attributes affect the end product. From choosing the finest components to carefully keeping track of fermentation, aging, and purification, artisans infuse their spirits with enthusiasm and knowledge.
In addition, artisanal craft distillers often embrace experimentation and innovation, pressing the limits of traditional spirits production. They may introduce unique taste profiles by integrating in your area sourced ingredients or utilizing innovative aging methods. This commitment to creativity and excellence lead to spirits that are not only of exceptional quality yet also display the artistry and individuality of the distiller.
Developments in Aging Strategies
One noticeable technology getting grip is the usage of smaller barrels for maturing spirits. By raising the surface area area-to-volume ratio, smaller barrels present flavors much more swiftly, resulting in a more intense growth process. This technique is especially popular amongst craft distillers seeking to produce top quality spirits in a much shorter timeframe.
Moreover, distillers are increasingly turning to different wood types, such as cherry or acacia, to give unique flavors to their aged spirits. These unusual timbers provide an unique taste profile, establishing their products apart in a competitive market.
Furthermore, improvements in innovation have actually made it possible for distillers to explore increased maturing techniques, such as ultrasound or temperature level and stress variations. These methods permit exact control over the aging procedure, resulting in innovative taste accounts that press the boundaries of typical spirits manufacturing.

The Role of Yeast in Fermentation
An essential component of the fermentation procedure in distilling is the role played by yeast. Yeast, a single-celled bacterium, is essential in transforming sugars right into alcohol and co2 during fermentation. In the context of distilling spirits, yeast plays a critical duty in the manufacturing of ethanol, which is the primary alcohol in the majority of alcoholic beverages.
Yeast achieves this with the procedure of anaerobic respiration, where it metabolizes sugars such as sugar and fructose right into ethanol and carbon dioxide. Various pressures of yeast can impart distinct flavors and scents to the final spirit, adding to the complexity and character of the distilled item. Distillers very carefully pick yeast stress based on their desired flavor account and fermentation characteristics.
The fermentation procedure can last anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on elements such as yeast sugar, stress, and temperature level material. Surveillance and managing the fermentation process are important to ensure optimum yeast activity and alcohol manufacturing. In general, yeast is a basic gamer in the alchemical makeover of raw components right into the spirited elixirs enjoyed by customers worldwide.
Lasting Practices in Distilleries
In the modern-day distilling industry, applying lasting techniques has actually come to be a pushing concern for distilleries looking for to lower their environmental effect and make certain long-lasting practicality. Distilleries are significantly acknowledging the relevance of taking on eco-friendly actions throughout the manufacturing process. One vital aspect of sustainability in distilleries is water preservation. Distilleries call for considerable quantities of water for numerous phases of production, and executing water recycling systems or making use of rain harvesting strategies can considerably minimize water usage and reduce the distillery's general environmental footprint.
In addition, lasting power sources are obtaining traction in the distilling globe. Several distilleries are spending in renewable resource technologies such as photovoltaic panels or biomass central heating boilers to lower dependence on non-renewable energy sources and lower greenhouse gas discharges. Furthermore, waste management practices play an essential role in sustainable distillery operations. Distilleries are checking out cutting-edge ways to repurpose byproducts such as spent grains or purification deposits, transforming waste right into sources with approaches like animal feed manufacturing or composting. By embracing sustainable methods, distilleries can not just minimize their environmental influence yet also attract eco mindful customers and add to a more sustainable future for the sector.
Conclusion
In web link verdict, the detailed characteristics of look what i found distillery operations entail a mix of scientific principles and imaginative craftsmanship. From the chemistry of distillation to the role of yeast in fermentation, distilleries are regularly trying out and innovating to develop premium spirits. By incorporating sustainable techniques and accepting brand-new aging methods, distilleries are forming the future of the market. The blend of practice and advancement in spirits manufacturing highlights the intricacy and imagination associated with this old craft.
As the drapes are drawn back on the complex globe of distillery dynamics, an interesting realm emerges where scientific research and art assemble to develop the spirits we savor.The chemistry of distillation, an essential process in the production of spirits, involves the splitting up of parts based on their different boiling points.Moreover, artisanal craft distillers often accept trial and error and advancement, pressing the limits of standard spirits manufacturing. In the context of distilling spirits, yeast my review here plays an essential function in the manufacturing of ethanol, which is the primary alcohol in the majority of alcoholic beverages.
From the chemistry of purification to the function of yeast in fermentation, distilleries are frequently introducing and trying out to develop high-quality spirits.